Clomid for Fertility

Clomid, also known as Serophene or clomiphene citrate, is an oral medication commonly used to treat certain types of female infertility and is occasionally used to improve male fertility. Clomid is usually prescribed as a first course of action to women struggling to get pregnant by their primary care provider, OBGYN, and some fertility clinics.
For women, Clomid is used to manage and treat anovulatory or oligo-ovulatory infertility and to induce ovulation for patients who are trying to get pregnant. Clomid also helps to increase the ovarian production of an egg follicle or multiple follicles.
Fast Facts on Clomid
- Clomid is the most commonly used fertility drug. Clomid is administered in pill form. Most stronger fertility drugs require injections.
- Clomid is an ovulatory stimulant that helps the body produce more mature eggs per cycle and assists with ovulation.
- Clomid may also be sold as Serophene or under its generic name, Clomiphene Citrate.
- In some trials, Clomid has been observed to stimulate ovulation in over 80% of participants .
- Clomid is commonly used with timed intercourse, IUI treatment, and mini IVF.
- Clomid is used to treat some forms of male factor infertility.
- While many OBGYNs and Fertility Clinics still prescribe Clomid, many Reproductive Endocrinologists have shifted from prescribing Clomid to Letrozole for female infertility because they have similar odds of producing a live birth, and letrozole generally has fewer side effects and produces more singleton births.
Who Should Take Clomid
Clomid is commonly prescribed to women with ovulatory disorders who either ovulate irregularly or do not ovulate at all (anovulation.) Patients undergoing fertility treatments such as timed intercourse, IUI, or mini IVF may also be prescribed Clomid to increase the number of mature eggs produced and thus improve the odds of conception. Many infertility patients with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) are prescribed Clomid to stimulate ovulation.
Clomid is used to treat male infertility when men have low sperm counts, especially when caused by low testosterone.
PCOS and Other Ovulatory Disorders
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal endocrine disorders in women, and is the number one cause of infertility – accounting for approximately 20-25% of all cases of infertility. Women with PCOS commonly experience hormonal imbalances, which impedes ovulation. Most women with PCOS ovulate irregularly or not at all.
Clomid is usually the first medication that is prescribed to PCOS patients (though Letrozole is usually a better option – more on this later). Clomid is well known to increase ovulation regularity and the chances of achieving pregnancy for women with PCOS.
Unexplained Infertility
Clomid citrate is also prescribed to patients with unspecified infertility in combination with insemination (IUI). Women who have normal fallopian tubes, regular 28-day cycles, and partners with a normal sperm count, but are still experiencing infertility, are termed as having ‘unexplained infertility.’
Some clinics prescribe Clomid to treat unexplained infertility, but it is often less effective than other alternative treatments. Clomid is usually prescribed as a first treatment because it is cost-effective, has minimal side effects, and because of its convenience. Unlike other more intensive treatments, Clomid is administered in pill form and can be prescribed by an OBGYN or primary care provider.
Male Factor Infertility
Clomid can be used to treat male infertility, specifically for men with low sperm counts caused by low testosterone levels. Clomid increases FSH production (increasing sperm production) and LH (testosterone production), leading to better sperm production and function. Taking Clomid is one of many ways that men can boost their fertility.
How does Clomid Work to Improve Fertility?
Clomiphene can cause women to produce several eggs each month and can help stimulate ovulation for women who don’t ovulate normally. Clomid works by tricking the body to think its estrogen levels are lower than they are. This causes the body to produce excess hormones that stimulate the ovary to produce more mature eggs to be released during ovulation.
By producing and releasing more eggs each month, there are more targets for sperm to shoot at it, thus increasing fertilization chances.
Mechanism of Function
Clomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator. It selectively binds to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, ovary, endometrium, and cervix . Clomid also acts as a partial estrogen agonist in the hypothalamus, causing an estrogenic negative feedback inhibition. This means that Clomiphene causes the brain to misinterpret blood estrogen levels. When the hypothalamus senses low estrogen levels, it triggers the pituitary gland to increase gonadotropin (LH and FSH) production.
The pituitary gland regulates the amount of gonadotropins in the system, specifically luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These two hormones play a key role in ovulation. LH and FSH levels influence when and how many eggs are developed and released. LH is responsible for the further maturation and release/ovulation of the egg(s).
When the pituitary gland increases FSH and LH production, it stimulates the follicles’ development, which contain the egg(s). The result is the production of multiple follicles, each of which contains an egg. Usually, a single egg follicle is activated in a normal unmedicated cycle, the egg grows and matures, and then it is released from the ovary. Clomid causes multiple follicles to mature so that multiple eggs are ovulated.
By increasing the amount of LH and FSH the body produces, Clomid can help to increase both ovulation and egg development.
Clomid and Fertility Treatments
As mentioned above, Clomid is one of the most common fertility medications. Unlike other medications, Clomid is often prescribed by your OBGYN or primary care provider. You are less likely to be prescribed Clomid if you are under the care of a fertility specialist, but it is still used along with some fertility treatments.
Fertility Testing
The first step in fertility treatment is both male and female fertility testing. The male partner will undergo a semen analysis to ensure the viability and health of his sperm. The female partner will undergo blood tests and an ultrasound to evaluate her egg supply, ovarian function, and the anatomy of the reproductive structures.
If the man’s results indicate that he has a low sperm count, a blood test may be performed and if it is determined he has low testosterone, he may be prescribed Clomid, but more on that later. After the clinician reviews the couple’s fertility testing results, they will recommend the appropriate treatment.
Timed Intercourse and Clomid
Since timed intercourse cycles are a relatively natural fertility solution, it is usually recommended for couples who have already undergone male and female fertility testing and have received ‘normal’ results or for those looking for a low cost solution prior to testing. Timed intercourse is the simplest fertility treatment available. It involves using ultrasound and blood work monitoring (or even a home ovulation predictor kit) to monitor follicular development and egg growth. By monitoring egg development and hormone levels, physicians are able to identify the window of time in which the woman is ovulating (when fertilization is most likely to occur.) This allows couples to engage in sexual intercourse at the time, which gives them the best chance of getting pregnant.
Clomid can be used along with timed intercourse cycles. Fertility specialists may prescribe Clomid or other fertility medications to stimulate egg production by the ovaries, induce ovulation, and improve chances for natural conception.
Clomid and Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
IUI treatment is usually recommended to couples who haven’t been able to get pregnant after multiple timed intercourse cycles or for couples where the male partner may have sperm motility issues. Similar to a timed intercourse cycle, Clomid may be prescribed alongside IUI treatment to stimulate egg growth and help time your ovulation with the insemination.
During IUI treatment, sperm is collected, concentrated, and deposited into a woman’s uterus. IUI treatment aims to increase the number of sperm that reach the uterus and then the fallopian tubes to increase the chance that successful fertilization will occur. Clomid is again used to increase the number of eggs available for fertilization and improve ovulation.
Thus more bullets are shooting at more targets.
How to use Clomid – Protocols and Dosing
Of course, it is important to follow the guidance of your medical provider when taking Clomid, so please using the following for general information purposes only. Clomiphene is taken as a pill, usually as the brand name Clomid, and is generally prescribed as one (50mg) pill each day for 5 days at the beginning of the menstrual cycle (starting day 2-4 and continuing for 5 days). A mature follicle is usually found around day 12 of the cycle. If Clomid does not cause ovulation to occur, then the medication can be changed to reflect the patient’s needs.
Ultrasound is used to monitor the number and maturity of the follicles. Ovulation predictor kits can also be used to measure if there has been a surge of LH mid-cycle, indicating ovulation is occurring. Ovulation occurs about 24-28 hours after the detection of the LH surge in the urine.
Natural (timed intercourse) or artificial insemination (IUI) is performed approximately 12-36 hours after the LH surge is detected (or a trigger medication is taken).
It is important to note that it is best to use Clomid for no more than 3 continuous months. After three months of continuous use, it is best to take 1-2 month break, then resume this pattern on repeat until pregnancy is achieved.
Clomid Success Rates
Research has shown that Clomid can induce ovulation in 80% of anovulatory women, but less than 40% of those women became pregnant . Clomid can help a high percentage of women ovulate, but that doesn’t guarantee pregnancy will occur. Clomid pregnancy rates are usually between 10-20% but can be as high as 60% after 6 cycles .
As with all fertility treatments, Clomid success rates are highly dependent upon age. Research has shown that Clomid is a more effective treatment to induce ovulation and result in pregnancy for women under the age of 35 compared to women in their early 40s. In one study, researchers treated participants with Clomid and IUI and compared the per-cycle pregnancy rates for different age groups. Women under 35 years old yielded a pregnancy rate of 11.5% per cycle. Only 1% of participants over the age of 42 were able to achieve pregnancy with Clomid and IUI treatment.
Because success rates are generally very low for those over 40, gonadotropin injections and IVF are usually recommended as a first course of action for women over the age of 40.
Clomid Resistance
Unfortunately, Clomid does not work for all women regardless of their age. Sometimes, fertility specialists will prescribe Metformin (an oral medication commonly used to treat diabetes) to be taken in conjunction with Clomid. Using clomiphene and Metformin together can be beneficial to stimulate ovulation for some women, especially those with PCOS.
Women who are unable to ovulate after taking Clomid are considered “Clomid resistant” and are usually prescribed different medications to induce ovulation. Fertility specialists may prescribe an alternative oral medication like Letrozole, which has been found to help Clomid-resistant women to ovulate. Depending on the patient and their treatment goals, the fertility specialist may instead recommend injectable medications like Gonadtropins.
Clomid for Men
Clomid can help male fertility in a couple of ways. It can help increase sperm count levels and also to correct hormonal imbalances, especially low testosterone. By increasing a man’s sperm count, he may have a better chance of conceiving naturally or through IUI treatment.
Clomid helps to improve sperm production by increasing the amount of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) the body produces. Similarly, it helps to improve testosterone levels by increasing the amount of Luteinizing hormone the body produces. Research has shown that increasing LH and FSH increases both testosterone production as well as spermatogenesis in men with low testosterone .
A study published on the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) website measured Clomiphene Citrate treatment’s effectiveness in men with idiopathic oligozoospermia and infertility. Participants in the study who were treated with Clomiphene Citrate saw a higher increase in sperm count and progressive sperm motility when compared with the control group. The treatment group also experienced a 37% pregnancy rate, nearly three times that of the control group (13%) .
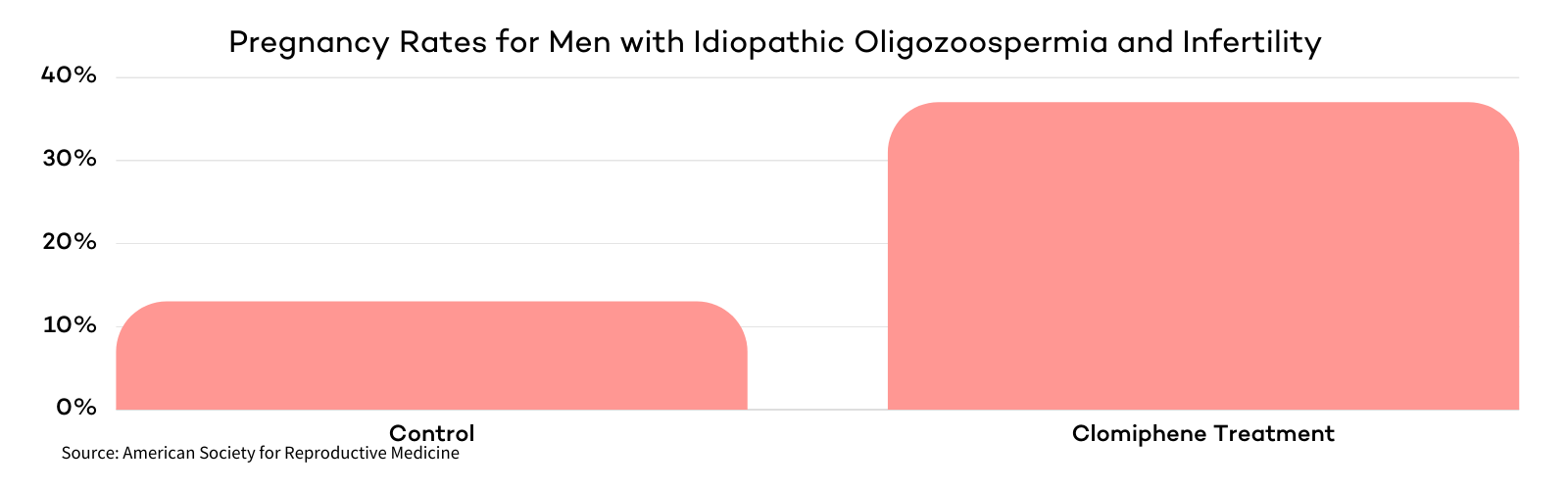
Clomid Price
Clomid is the least expensive fertility drug and costs between about $10 and $100 per cycle depending on the dose and whether a brand name or generic clomiphene citrate is used. Clomid is usually covered by your insurance, even when other fertility medications are not. Please be sure to speak with your doctor about finding Clomiphene for an affordable price and ask about other options that may produce more beneficial results.
Clomid V.S. Letrozole
Similar to Clomid, Letrozole is an aromatase inhibitor (lowers estrogen production) that can be used to induce ovulation in patients with irregular ovulation patterns or those who suffer from anovulation. Letrozole improves ovulation by blocking estrogen production, which causes additional FSH and LH to be released.
Research on both Letrozole and Clomiphene to treat infertility in patients suffering from ovulatory issues is extensive. Studies have shown that both medications can increase ovulation regularity and the chances of achieving pregnancy. However, recent research has indicated that letrozole is more effective than clomiphene for inducing ovulation and increasing pregnancy chances, especially for women with PCOS.
A study conducted by the National Institute of Health (NIH) found that PCOS patients treated with Letrozole experienced higher ovulation and live birth rates compared to women treated with clomiphene. In the study, 374 women were treated with Letrozole, and 103 (27.5%) of these women had a live birth. 376 women were treated with Clomiphene, but only 72 (19.1%) of these women had a live birth .
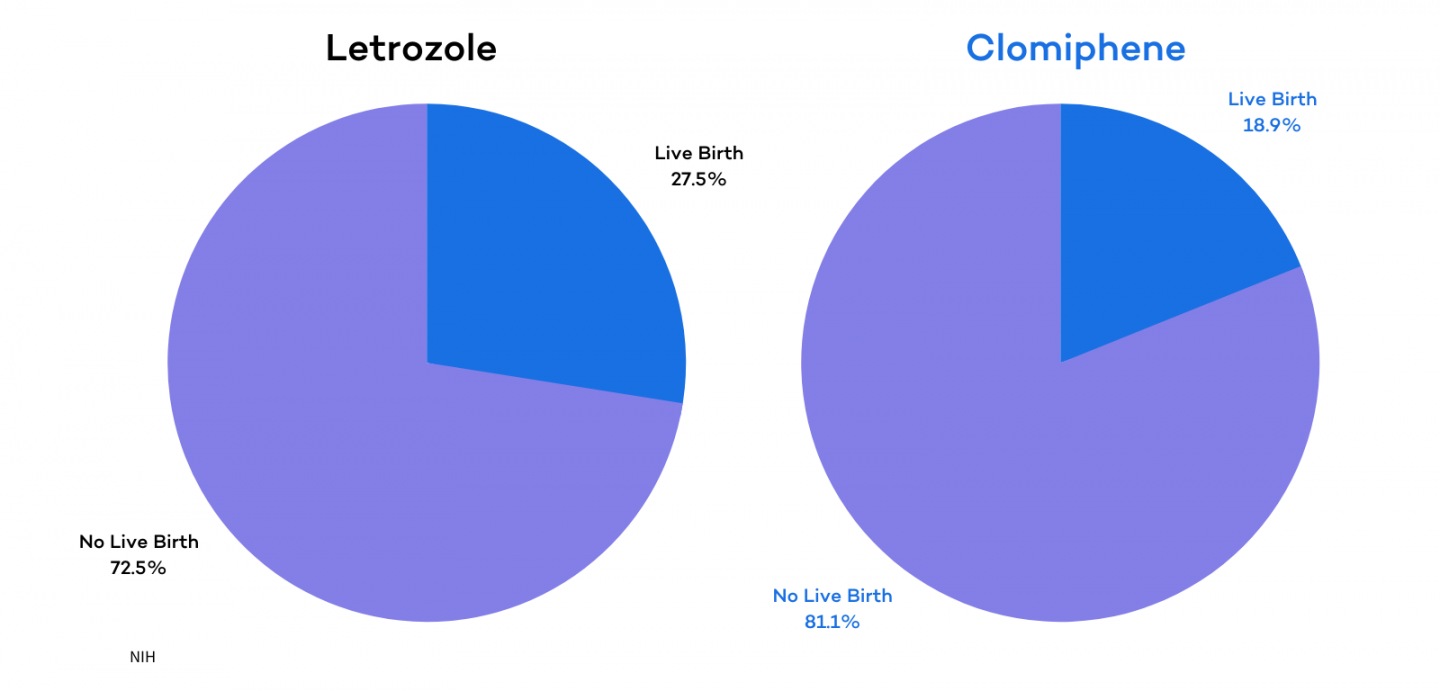
In addition to producing higher ovulation and live birth rates than Clomiphene, Letrozole was also observed to produce lower instances of twins in this study. Since both Clomiphene and Letrozole increase the number of eggs the body produces, they also increase the chances of having twins (one of the main risks of taking fertility medications.) by 3.4% of the letrozole group, and 7.4% of the clomiphene group resulted in twin pregnancies. More than double the number of participants treated with Clomiphene became pregnant with twins when compared to the Letrozole group.
Due to the new research surrounding the success rate of Letrozole compared to Clomiphene and the lower instance of twin pregnancies, many fertility clinics, including CNY Fertility, have shifted from prescribing Clomid to Femara (brand name of Letrozole) for female infertility.
Other Fertility Medications
There are several different fertility medications available that can be used along with fertility treatments or to increase the chances of natural conception. To discover which medication fits your fertility treatment goals best, we recommend scheduling a consultation appointment with a fertility specialist. Your fertility doctor will review your fertility testing results, past fertility and medical history, and all other available information to determine the appropriate treatment and medication protocol for you. Please find a brief review of some fertility medications we commonly prescribe at our clinics below:
Letrozole (Femara): Originally developed as a breast cancer medication, letrozole is usually the best choice to stimulate the ovaries during an ovulation induction timed intercourse cycle and IUI cycles. Similar to Clomid, Letrozole works by increasing the amount of FSH the pituitary gland secretes.
Metformin (Glucophage, Fortamet, others): An oral medication for type two diabetes helps improve insulin resistance and lower insulin levels. Though it may not seem related to infertility, metformin has been shown to help tremendously those who do not ovulate regularly or have PCOS.
Gonadotropins: Injectable medications are usually encountered after failed IUIs. They can be used with both IUI and IVF cycles.
In Conclusion
Clomiphene Citrate, Clomid, or Serophene are commonly prescribed fertility medications that can increase ovulation and the number of eggs a woman produces each month as well as improve sperm in men with low testosterone. For women, it generally work best for patients who have ovulatory issues like those who are diagnosed with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS).
Clomid has been used to treat infertility since the 1960s, and although it may be the oldest medication used to treat infertility, that doesn’t mean it is the best. If you are prescribed Clomid as a female, be sure to ask your doctor about other available fertility medications, especially Letrozole.


