The Ultimate Glossary of Fertility Acronyms
Embarking on the journey of fertility and trying to conceive (TTC) can feel like diving into a world with its own unique language. The fertility community frequently relies on dozens of acronyms and abbreviations to communicate about different aspects of the complex process of getting pregnant and giving birth.
To help you feel more comfortable and confident as you navigate these conversations, here’s a guide to some of the most widely used fertility acronyms and what they mean.
ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology): Treatments like IVF that assist conception by manipulating eggs, sperm, or embryos outside the body.
AI (Artificial/Assisted Insemination): Placing sperm directly in the reproductive tract to increase chances of fertilization, often timed with ovulation.
AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone): AMH is a hormone that reflects ovarian reserve, indicating the number of eggs left.
BBT (Basal Body Temperature): Body’s resting temperature, tracked daily to pinpoint ovulation based on subtle rises after ovulation.
BD (Baby Dance): Euphemism for sex when the aim is to conceive.
Beta (hCG Pregnancy Test): Blood test measuring hCG (pregnancy hormone) levels to confirm and monitor early pregnancy progress.
BFN (Big Fat Negative): A negative pregnancy test result, often a disappointing outcome for those TTC.
BFP (Big Fat Positive): A positive pregnancy test result, signaling pregnancy.
BPM (Beats Per Minute): Refers to the fetal heart rate, typically measured during ultrasounds.
B/W (Bloodwork): Blood tests used to assess hormone levels, ovulation, pregnancy, or overall fertility health.
CASA (Computer-assisted Semen Analysis): Advanced test that analyzes sperm health using computer imaging for accuracy.
CB (Cycle Buddy): A support partner going through a similar fertility treatment or menstrual cycle, providing emotional support.
CCCT (Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test): Evaluates ovarian reserve by stimulating the ovaries with Clomid (clomiphene) and measuring FSH response.
CD (Cycle Day): Refers to a specific day within the menstrual cycle, with Day 1 being the first day of menstruation.
CM (Cervical Mucus): Fluid in the cervix that changes in consistency throughout the cycle, indicating fertile days when it resembles raw egg whites.
CNM (Certified Nurse Midwife): A nurse with advanced training in pregnancy, birth, and reproductive health, often working with OB/GYNs or independently.
COHS (Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation): Using medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs for procedures like IVF.
CP (Cervical Position): The position of the cervix, which moves and changes texture during different cycle stages, is often used to predict ovulation.
DE (Donor Eggs): Eggs donated by another woman, often used when an intended mother has low ovarian reserve or genetic concerns.
DEIVF (Donor Egg IVF): IVF using donated eggs, fertilized in the lab, and transferred to the recipient’s uterus.
DH (Dear Husband): A common term of endearment used for one’s spouse or partner in the fertility community.
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone): A hormone sometimes prescribed to improve ovarian function in women with low ovarian reserve.
DI (Donor Insemination): Artificial insemination using sperm from a donor.
DIPI (Direct Intraperitoneal Insemination): Placing sperm into the pelvic cavity, near the fallopian tubes, to aid fertilization.
DOR (Diminished Ovarian Reserve): Lower-than-expected egg supply, impacting fertility potential.
DP (Dear Partner): Similar to DH, a supportive term for one’s partner or spouse.
DPO (Days Post-Ovulation): Counting the days after ovulation, often used to track early pregnancy symptoms or testing days.
DPR (Days Post-Retrieval): Days after eggs are retrieved in an IVF cycle, marking embryo development progress.
DPT (Days Post-Transfer): Days after embryo transfer in an IVF cycle, a time of waiting for pregnancy confirmation.
DP3DT (Days Post 3-Day Transfer): Days since a 3-day embryo transfer, referring to embryos cultured for three days before being placed in the uterus.
DP5DT (Days Post 5-Day Transfer): Days since a 5-day embryo transfer, with embryos cultured for five days to the blastocyst stage.
DW (Dear Wife): Similar to DH, used affectionately for one’s wife or female partner.
Dx (Diagnosis): Identification of a condition or cause of fertility challenges.
E2 (Estradiol Level): A type of estrogen checked during treatment to monitor ovarian response.
EDD (Estimated Due Date): Expected date of childbirth, calculated from the LMP or conception date.
EMB (Endometrial Biopsy): A sample of the uterine lining to check for abnormalities or ensure readiness for embryo implantation.
ENDO (Endometriosis): A condition where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus, potentially affecting fertility.
EPT (Early Pregnancy Test): A home test that can detect pregnancy hormone (hCG) days before a missed period.
ER (Egg Retrieval): The process of collecting mature eggs from the ovaries during IVF.
ERA (Endometrial Receptivity Array): A test to determine the optimal window for embryo transfer based on uterine lining readiness.
ET (Egg/Embryo Transfer): Placing fertilized embryos into the uterus, often the final step in IVF.
ETA (Embryo Toxicity Assay): A test to identify potential toxic factors affecting embryo health.
ETF (Embryo Toxicity Factor): Factors that may harm embryo development, often assessed in lab tests.
EWCM (Egg White Cervical Mucus): Fertile cervical mucus that looks like raw egg whites, indicating high fertility.
FET (Frozen Embryo Transfer): Thawing and transferring a previously frozen embryo into the uterus.
FF (Fertility Friend): A popular fertility tracking app and community support tool.
FI (Fasting Insulin): Insulin level tested after fasting, sometimes checked when investigating fertility issues related to blood sugar.
FHR (Fetal Heart Rate): Heart rate of a developing fetus, often measured during prenatal care.
FP (Follicular Phase): First half of the menstrual cycle when follicles grow, leading up to ovulation.
FPG (Fasting Blood Plasma Glucose): Blood glucose level measured after fasting, relevant for assessing blood sugar health.
Frostie (Frozen Embryo): Term for a frozen embryo stored for later use.
FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone): Hormone responsible for stimulating ovarian follicles; tested to gauge ovarian function.
FTTA (Fertile Thoughts to All): A supportive phrase wishing fertility success for others in the TTC community.
GnRH (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone): Hormone involved in stimulating the release of FSH and LH.
GP (General Practitioner): A primary care doctor who may assist with initial fertility evaluations or referrals.
GTT (Glucose Tolerance Test): A test to measure the body’s response to sugar, used to screen for conditions like gestational diabetes.
hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): Hormone produced in pregnancy, detected in pregnancy tests.
hMG (Human Menopausal Gonadotropin): Fertility hormone that stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs, often used in ART.
HCP (Health Care Practitioner): Any medical professional providing fertility care or support.
HEPA (Hamster Egg Penetration Assay): Test of sperm’s ability to penetrate an egg-like structure.
HPT (Home Pregnancy Test): At-home test to detect hCG, confirming pregnancy.
HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy): Hormones provided to supplement the body’s natural levels, sometimes used in fertility care.
HSC (Hysteroscopy): Procedure to view and assess the inside of the uterus.
HSG (Hysterosalpingogram): X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes to detect blockages or issues.
HX (History): Medical history, often reviewed in fertility assessments.
IBT (Immunobead Binding Test): A test to detect antibodies against sperm, which could impact fertility.
ICI (Intracervical Insemination): Procedure where sperm is placed directly into the cervix to aid conception, a step below IUI.
ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection): An IVF procedure where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg to assist fertilization.
IF (Infertility): The inability to conceive after a year of trying (or six months if over age 35).
IM (Intramuscular Injection): An injection administered into the muscle, often used for medications like progesterone in fertility treatments.
ITI (Intratubal Insemination): Sperm is placed directly into the fallopian tube, closer to where fertilization occurs naturally.
IUGR (Intrauterine Growth Retardation): A condition where a fetus grows slower than expected in the womb, potentially affecting pregnancy outcomes.
IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): A fertility procedure where sperm is placed directly in the uterus to improve chances of fertilization.
IVC (Intra-vaginal Culture): A technique where eggs and sperm are cultured together in a vaginal incubator to facilitate fertilization.
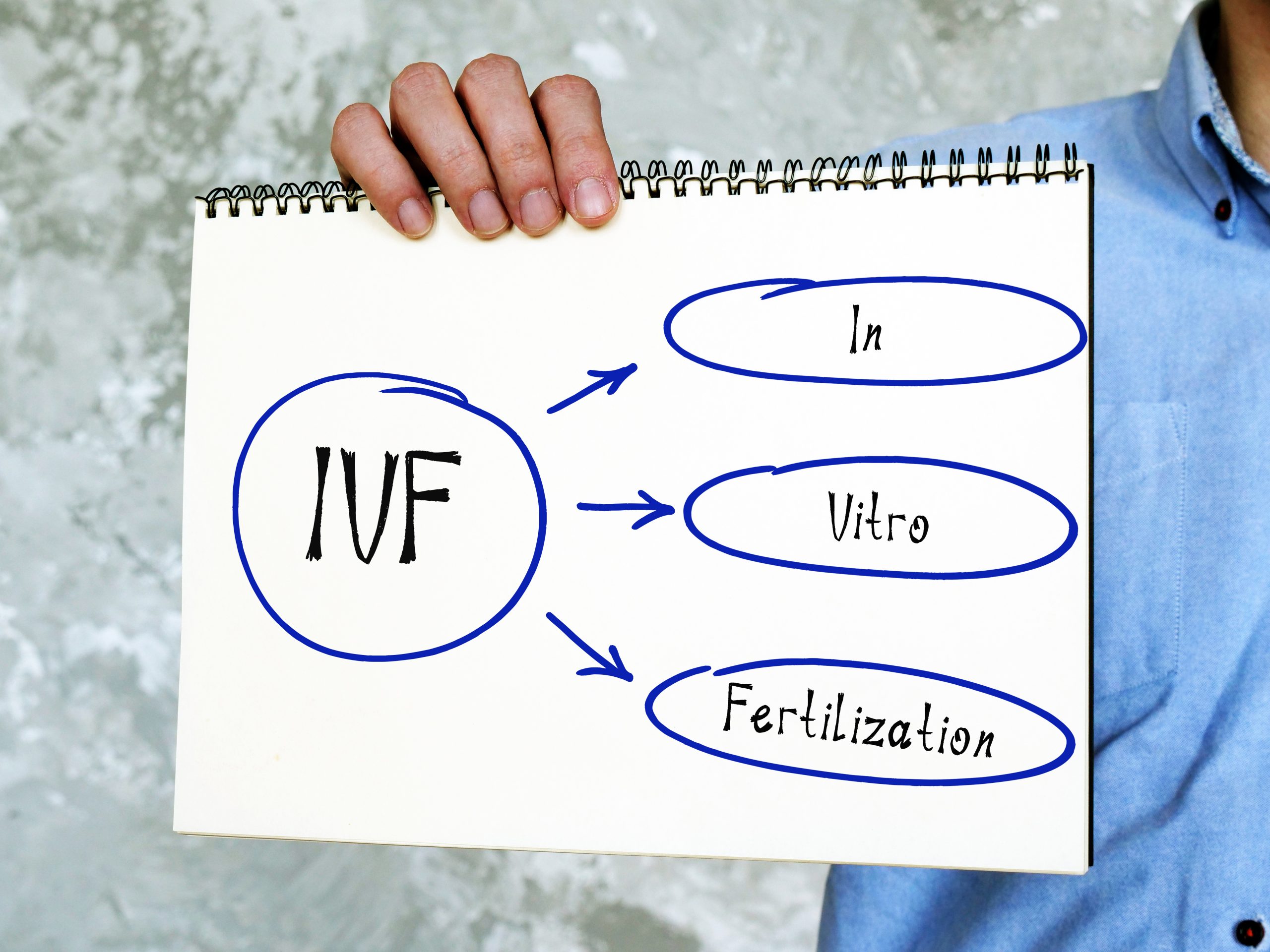
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization): Fertility treatment where eggs and sperm are combined in a lab to create embryos.
IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin): An immune therapy used in some fertility treatments to address immune-related infertility.
LAD (Leukocyte Antibody Detection Assay): A test for immune response in which antibodies against white blood cells are measured.
LAP (Laparoscopy): A minimally invasive surgical procedure often used to diagnose or treat issues like endometriosis or ovarian cysts.
LH (Luteinizing Hormone): A hormone that triggers ovulation and is essential for reproductive function.
LIT (Leukocyte Immunization Therapy): An immune therapy used in some cases of recurrent pregnancy loss or infertility.
LMP (Last Menstrual Period): The first day of your last menstrual period, commonly used to calculate pregnancy dating.
LP (Luteal-Phase): The second half of the menstrual cycle after ovulation, crucial for implantation and early pregnancy.
LPD (Luteal-Phase Defect): A condition where the luteal phase is too short or hormone levels are insufficient, affecting implantation.
LSP (Low Sperm Count): A lower-than-normal concentration of sperm, which can impact fertility.
LUF (Luteinized Unruptured Follicle Syndrome): A condition where the follicle doesn’t release an egg despite luteinization, affecting ovulation.
MAI (Miscarriage after Infertility): Refers to pregnancy loss experienced by those who have struggled with infertility.
MC (Miscarriage): The loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week.
MENTS (Subject Matter May Be Difficult to Read): A courtesy warning on forums when discussing sensitive topics, like loss or trauma.
MESA (Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration): A procedure to collect sperm directly from the epididymis in men with obstructive azoospermia.
MF (Male Factor): Refers to infertility issues originating from the male partner, such as low sperm count or motility.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Imaging technique sometimes used to diagnose fertility issues, like tumors or endometriosis.
NK (Natural Killer Cells): Part of the immune system that, in high levels, may impact implantation and pregnancy.
NORIF (Non-stimulated Oocyte Retrieval In-office Fertilization): Egg retrieval performed without stimulation drugs, used in special fertility cases.
NP (Nurse Practitioner): A licensed nurse with advanced training, who may assist in fertility treatments.
NSA (Non-Surgical Sperm Aspiration): A less invasive technique for collecting sperm.
O, OV (Ovulation): The release of an egg from the ovary, essential for natural conception.
OB (Obstetrician): A doctor specializing in pregnancy and childbirth.
OB/GYN (Obstetrician/Gynecologist): A doctor specializing in reproductive health, pregnancy, and childbirth.
OC (Oral Contraceptives): Birth control pills, sometimes used to regulate cycles before fertility treatments.
OD (Ovum Donor or Ovulatory Dysfunction): Refers to an egg donor or a condition impacting ovulation.
OHSS (Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome): A reaction to fertility drugs where ovaries become swollen, sometimes requiring medical attention.
OI (Ovulation Induction): Stimulating ovulation through medications to improve chances of conception.
OPT (Ovulation Predictor Test): This test checks for hormonal changes signaling ovulation.
OTC (Over the Counter): Non-prescription medications or tests, like home pregnancy tests.
P4/Prog (Progesterone): A hormone supporting the uterine lining in early pregnancy.
PAI-1 (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1): A protein that may be tested in cases of recurrent pregnancy loss.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome): A hormonal disorder affecting ovulation, linked to insulin resistance and fertility challenges.
PCP (Primary Care Physician): Your main healthcare provider, who can provide referrals for fertility specialists.
PCT (Post-Coital Test): Examines cervical mucus after intercourse to check sperm’s ability to survive and move.
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration): A technique for collecting sperm directly from the epididymis.
PG (Pregnant): Being in a state of pregnancy.
PGD (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis): Genetic testing on embryos to screen for specific genetic conditions.
PGS (Preimplantation Genetic Screening): Genetic testing of embryos to check for chromosomal abnormalities.
PGT (Preimplantation Genetic Testing): An umbrella term for testing embryos for genetic or chromosomal health before transfer.
PI (Primary Infertility): Infertility in couples who have never conceived before.
PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease): Infection in the reproductive organs, which can impact fertility.
PIO (Progesterone in Oil): A progesterone injection used to support pregnancy in fertility treatments.
PLI (Paternal Leukocyte Immunization): An immune treatment sometimes used for recurrent miscarriage.
PMN (Perinatal Mortality): Refers to death around the time of birth, including stillbirth or neonatal death.
POAS (Pee On A Stick): Taking a home pregnancy test.
POI (Premature Ovarian Insufficiency): When the ovaries stop functioning before age 40, affecting fertility.
PPROM (Preterm Premature Rupture of the Membranes): Early breaking of waters, leading to preterm birth risks.
PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder): Anxiety disorder from traumatic experiences, sometimes seen after pregnancy loss.
PUPO (Pregnant Until Proven Otherwise): Mindset after embryo transfer, hopeful until pregnancy is confirmed.
PZD (Partial Zona Dissection): Assisted reproductive technique used in some IVF cases to help sperm fertilize an egg.
RE (Reproductive Endocrinologist): A specialist in fertility and hormonal issues related to reproduction.
R-hFSH (Recombinant Human Follicle Stimulating Hormone): A synthetic version of FSH used to stimulate egg production in fertility treatments.
RI (Reproductive Immunologist): A doctor who focuses on immune-related fertility issues, such as recurrent miscarriage or implantation failure.
RPL (Recurrent Pregnancy Loss): Multiple miscarriages, often defined as three or more consecutive losses.
RX (Prescription): Medication prescribed by a healthcare provider, often seen in fertility treatment plans.
SA (Semen Analysis): A test that assesses sperm count, motility, morphology, and other factors in a semen sample to evaluate male fertility.
SART (Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology): An organization that provides standards, data, and support for ART clinics and patients.
SB (Stillbirth): The loss of a fetus after the 20th week of pregnancy.
SD (Sperm Donor): A man who donates sperm for use in assisted reproductive procedures, like IUI or IVF.
SHG, SIS (Sonohysterogram or Saline Infusion Sonogram): An ultrasound test with saline to visualize the uterus and check for abnormalities.
SI (Secondary Infertility): Difficulty conceiving or carrying a pregnancy to term after previously giving birth.
SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus): An autoimmune disease that can impact fertility and pregnancy.
SO (Significant Other): Refers to one’s partner, often used in fertility communities.
SPA (Sperm Penetration Assay): A test assessing sperm’s ability to penetrate an egg-like structure, gauging fertility potential.
SPALS (Subsequent Pregnancy After a Loss Support): Support groups for those who are pregnant after experiencing a loss.
S/S (Signs/Symptoms): Refers to physical indicators or symptoms, often discussed in relation to fertility treatments or early pregnancy.
STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease): Infections passed through sexual contact, some of which can impact fertility.
SQ, SubQ (Subcutaneous Injection): An injection administered under the skin, often used for medications in fertility treatments.
SUZI (Subzonal Insertion): A type of assisted reproductive procedure where sperm is injected near the egg, similar to ICSI.
T1 (Type 1 Diabetes): Insulin-dependent diabetes that may impact fertility or pregnancy, often managed with careful blood sugar control.
T2 (Type 2 Diabetes): Insulin-resistant diabetes, which can affect fertility, especially in women with PCOS.
T4 (Thyroxine): A thyroid hormone tested and managed in some fertility treatments, as thyroid health impacts fertility.
TeBG (Testosterone-Estradiol Binding Globulin): A protein that binds to sex hormones, tested to understand hormonal health.
TDI (Therapeutic Donor Insemination): Insemination procedure using anonymous donor sperm to achieve pregnancy.
TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration): A procedure to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles, used in cases of male infertility.
TET (Tubal Embryo Transfer): Placing an embryo directly into the fallopian tube rather than the uterus, sometimes used in specific ART cases.
TI (Timed Intercourse): Planning sexual intercourse around ovulation to increase chances of conception.
TL (Tubal Ligation): A permanent form of birth control where fallopian tubes are cut or sealed, preventing pregnancy.
TORCH (Toxoplasmosis, Other, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes Test): A panel of tests to detect infections that could impact pregnancy.
TR (Tubal Reversal): Surgery to reverse a tubal ligation, allowing the possibility of natural conception.
TRH (Thyroid Releasing Hormone): A hormone that regulates thyroid function, sometimes tested in fertility evaluations.
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone): Hormone controlling thyroid function; imbalances can impact menstrual cycles and fertility.
TTC (Trying To Conceive): Actively attempting to get pregnant, often used by those pursuing natural or assisted conception.
TTCAR (Trying to Conceive After Reversal): Trying to conceive after reversing a prior sterilization, like a tubal ligation or vasectomy.
TWW (Two Week Wait): The period after ovulation or embryo transfer when one waits to see if conception has occurred.
TX (Treatment): Medical treatment, often seen in the context of fertility plans or interventions.
TZD (Thiazolidinediones): Medications sometimes used to manage insulin resistance, particularly in women with PCOS.
UR (Urologist): A doctor specializing in urinary and male reproductive health, often consulted for male fertility issues.
US (Ultrasound): Imaging technique used in fertility treatments to monitor follicles, uterus, or pregnancy progress.
UTI (Urinary Tract Infection): An infection in the urinary system that can cause discomfort but typically doesn’t affect fertility.
VR (Vasectomy Reversal): Surgery to reverse a vasectomy, allowing the possibility of natural conception.
WBC (White Blood Count): A blood test to measure immune cell levels, often part of health assessments.
WFP (Wait for Period): The period of waiting to see if menstruation arrives, signaling the start of a new cycle.
WHR (Waist to Hip Ratio): A health indicator that may relate to fertility and overall health, especially in PCOS assessments.
WIC (Where In Cycle): Term often used in fertility forums to discuss current cycle day or fertility status.
WNL (Within Normal Limits): Lab or test results that fall within normal, healthy ranges.
ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer): Fertilization occurs in a lab, then the zygote is placed in the fallopian tube, similar to TET.
This covers our comprehensive glossary for understanding fertility-related acronyms!
