The IVF Implantation Process: Everything You Need to Know
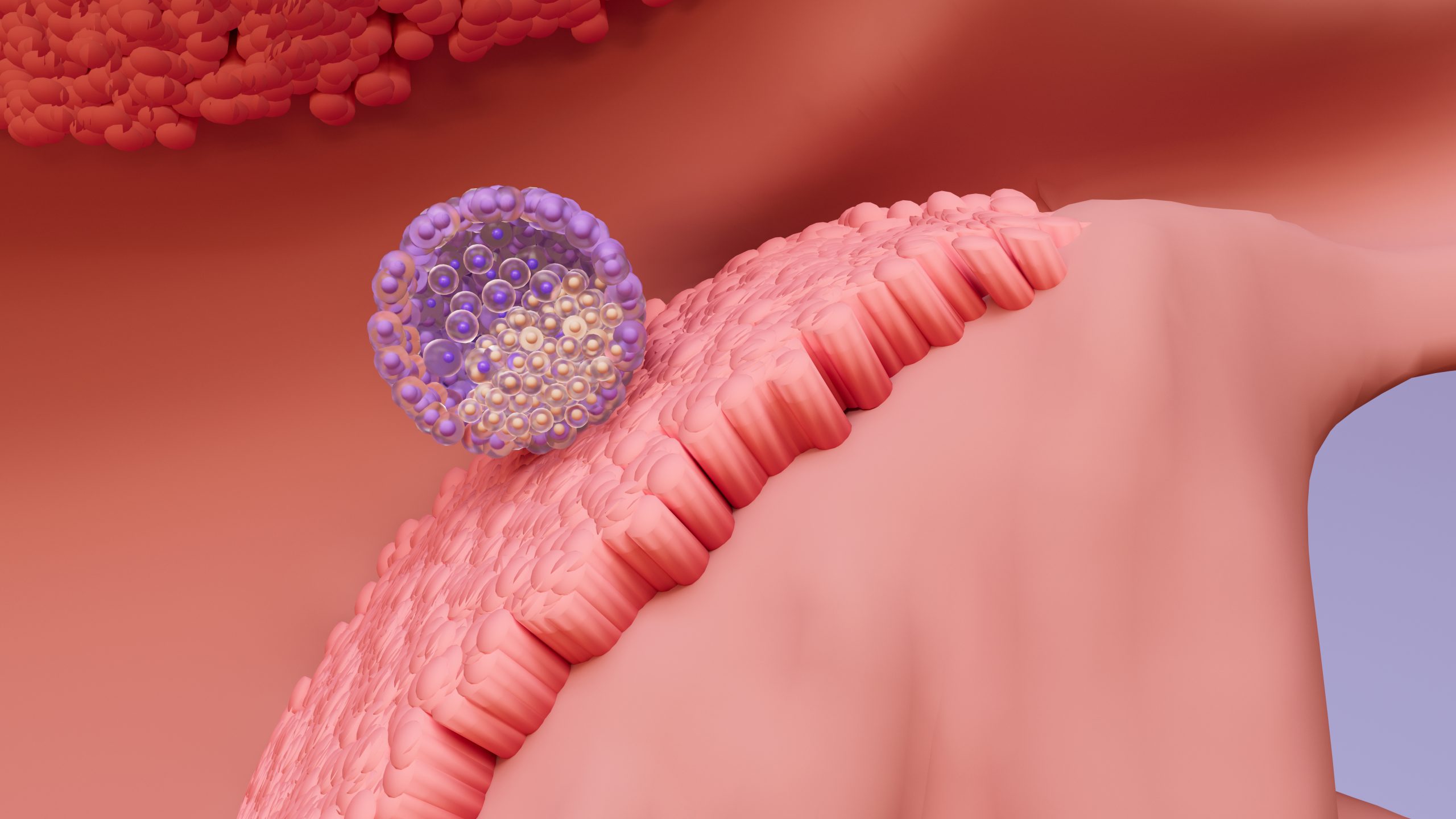
A critical step in the IVF process is implantation, where the fertilized embryo embeds itself into the uterine wall after it has been transferred to the uterus.
In this article, we’ll explore the science and strategies behind IVF implantation, and the factors that influence its success rates, including the best practices for maximizing the chances of implantation.
What is the Implantation Stage of IVF?
The implantation stage of IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) is a critical phase where the embryo attaches itself to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) and begins to grow.
Here’s a summary of the linked processes that constitute implantation:
Preparing the uterus for implantation: Estrogen supplements (pills, patches, or injections), and progesterone given orally, vaginally, or via injection, are usually recommended before embryo transfer to thicken and prepare the endometrium. These medications will continue until the 10th or 12th week of pregnancy. If undergoing a frozen transfer (FET), estrogen is started 2-4 days after the cycle starts (day 1 of the FET calendar). Progesterone is started around day 11 (this can vary depending on how quick or slow your uterine lining grows).
Monitoring: Monitoring: Blood tests monitor hormone levels, and vaginal ultrasounds check the endometrial thickness after approximately two weeks of estrogen use. A healthy endometrium is typically 7-8 mm thick and has a three-layered structure that is called “trilaminar”.
Embryo Transfer: After the female’s eggs are fertilized with sperm, they are cultured for 3 to 5 days in a laboratory. The embryos are then either transferred fresh or frozen (to be transferred at a later time) into the woman’s uterus. In this procedure, the embryo is loaded into a catheter, inserted through the cervix, and expelled along with a small portion of the transfer medium into the uterus.
Post-Transfer Period: Over the next few days, the embryo begins to make contact with the uterine lining, during which it “hatches” from its protective shell (zona pellucida) and begins to implant itself into the endometrial lining. There, the embryo connects with the mother’s blood supply, from which it receives the nutrients it needs to grow. [1]
Pregnancy Confirmation: Between 10-14 days after transfer, you will take a blood test at your clinic to check for pregnancy–the ultimate sign of a successful embryo implantation. This test is known as the “beta” or “beta hCG.” [2]
Implantation Timeline
Here’s a breakdown of a standard timeline in which the embryo embeds into the uterus [3] [4] :
- Day 1-3 Post-Transfer: The embryo moves towards the uterine cavity and prepares for implantation.
- Day 4-5 Post-Transfer: The embryo begins to hatch from its shell.
- Day 5-7 Post-Transfer: The embryo attaches to the uterine lining and starts the implantation process.
 Source: Ochoa-Bernal MA, Fazleabas AT. 2020
Source: Ochoa-Bernal MA, Fazleabas AT. 2020
What Factors Influence IVF Implantation Rates
There are several factors, both medical and lifestyle, that can influence IVF implantation rates.
Embryo quality
High-quality embryos are generally more likely to implant successfully and lead to a healthy pregnancy. The most significant factor impacting embryo quality is the female’s age when the eggs were retrieved. [5] [6]
Age
The younger the patient is when the eggs are retrieved, the higher the chance of successful implantation. [7]

According to the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART), the success rate of embryo implantation and live birth via IVF decreases with age [8] :
- Under 35: 51%–55.6% chance of live birth for a singleton (one child) using the patient’s own eggs
- 35–37: 38.3%–40.8% chance of live birth for a singleton using the patient’s own eggs
- 38–40: 25.1% chance of live birth for a singleton using the patient’s own eggs
- 41–42: 12.7% chance of live birth for a singleton using the patient’s own eggs
- Over 42: 4.1% chance of live birth for a singleton using the patient’s own eggs
Embryo Grades and Implantation Rates
A 2017 observational study involving over 1,700 single embryo transfers found a notable correlation between embryo grades and implantation rates [9] :
- Good Embryos: These had an implantation rate of 55% and a birth rate of 46.8%.
- Fair Embryos: These had an implantation rate of 47.2% and a birth rate of 39%.
- Poor Embryos: These had an implantation rate of 43.6% and a birth rate of 34.1%.
It’s important to remember that even embryos with a “poor” grade still have about a 1 in 3 chance of successfully implanting and resulting in a live birth.
It’s important to note that embryo grading is highly subjective. The process involves taking a picture of an embryo–which can be of poor image quality and only reveal one side of the embryo– making it a subjective designation. [10]
Genetic Testing
At the blastocyst stage, a 3-5 cell biopsy can be performed on the embryo to test for chromosomal abnormalities, ensuring the embryo has the correct number of chromosomes. This testing can also tell you the sex of each embryo if that is information you would like to know.
Preimplantation genetic testing is often recommended for people with a history of infertility or recurrent pregnancy loss, women over the age of 35, and those at risk for known genetic disorders or chromosomal issues.
A 2021 Study involving 4,515 patients undergoing up to three consecutive Single Embryo Transfers (SET) of PGT tested, chromosomally normal (euploid) embryos found [11] :
- 69.4% implantation rate during the first transfer.
- 59.3% implantation rate during the second transfer.
- 59.2% implantation rate during the third transfer.
- 94.9% chance of achieving pregnancy.

Assisted Hatching
At CNY, assisted hatching is a standard component of IVF. This technique is employed to help the embryo break through its outer shell and attach to the uterine lining. [12]
Assisted hatching can be especially beneficial for patients:
- with elevated FSH levels
- of advanced maternal age
- whose embryos have thick outer shells (zonas)
- preparing for a Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) with cryopreserved embryos.
Uterine Environment
A receptive uterine lining is crucial for implantation. Hormone levels, the thickness of the endometrium, and the absence of uterine abnormalities (like a polyp or uterine septum) and sources of inflammation such as endometriosis play significant roles. All of these factors can be assessed and, to a large extent, managed by fertility specialists prior to implantation. [13]
Day 3 vs Day 5 Embryos: Implantation Rates
A major debate in IVF has been whether to transfer embryos at the cleavage stage (day 3) or the blastocyst stage (day 5-7). These stages are often called “day 3” and “day 5” embryo transfers.
Embryo development sees significant attrition; for instance, a patient might start with 10 embryos on fertilization day, have 5 by day 3, and only 2 by day 5. Some patients may never produce day 5 embryos despite multiple IVF cycles.
Consequently, more embryos are typically available for transfer on day 3 than on day 5. However, blastocyst-stage (day 5) have marginally higher implantation rates due to their maturity and greater likelihood of being chromosomally normal.
A 2023 study out of Indonesia comparing day-3 and day-5 embryo transfers yielded the following statistics [14] :
Characteristic | Day-3 embryo transfer | Day-5 embryo transfer |
|---|---|---|
Clinical pregnancy rate (%) | 93/221 (42.1%) | 21/45 (46.7%) |
Implantation rate (%) | 134/511 (26.2%) | 31/94 (33%) |
Multiple pregnancy (%) | 36/221 (16.3%) | 9/45 (20%) |
Live birth rate – from embryos that implanted (%) | 102/134 (76.1%) | 23/31 (74.2%) |
Another study from 2000 comparing implantation rates between day 3 vs day 5 embryos found that:
- day 3 transfers had a 21% implantation rate
- day 5 Transfers had a 24% implantation rate
Despite these differences in implantation rates, the overall pregnancy rates per embryo transfer were identical at 39% for both day 3 and day 5 transfers. This indicates that there were no significant advantages in pregnancy outcomes compared to day 3 transfers. [15]
The implantation rates in the studies above include both single and multiple embryo transfers.
The takeaway from these studies is that although there is a prevailing belief that day 5 embryos are significantly better, statistical analysis indicates that the difference in implantation and live birth rates are similar.
Development and Transfer Protocol
At CNY Fertility, If the patient has five or more fertilized eggs on day 1, all are left to a culture in an attempt to form blastocyst embryos.
If the patient has four or fewer eggs on day 1, the embryos are either transferred on day 3 or frozen at day 3 for future use.
This protocol changes if a patient chooses to utilize PGT testing of embryos. Because genetic testing (PGT) requires a blastocyst embryo, CNY will attempt to grow embryos to the blastocyst stage for biopsy even if the patient has less than five fertilized eggs.
Fresh vs Frozen Embryos: Implantation Rates
Embryos are transferred either fresh or frozen. A fresh transfer typically takes place 3-7 days after the egg retrieval.
With a fresh transfer, usually 1-2 embryos are transferred (depending on patient age) while the rest (if any) are frozen.
You can use the frozen embryos later if the fresh transfer isn’t successful or if you want to have more children. With a frozen transfer, all embryos are frozen at the cleavage or blastocyst stage and transferred during a subsequent menstrual cycle.
When comparing the implantation rates for fresh vs. frozen embryos, a 2017 study comparing data from numerous fertility centers found that frozen embryos had a higher rate of implantation and pregnancy rates (52%) than fresh embryos (45.3%). [16]
CNY is generally an advocate of fresh transfers if:
- the uterine lining is greater than 7 or 8 mm
- estrogen and progesterone levels are within a safe and effective range
- the patient didn’t produce excessive follicles/eggs
IVF Implantation: The Takeaway
The implantation phase, where the fertilized embryo embeds into the uterus, is a crucial step in the IVF process.
Successful implantation involves preparing the endometrium with hormones, carefully timing the embryo transfer, and ensuring the uterine environment is optimal. Factors such as the patient’s age, embryo quality, and the use of techniques like assisted hatching significantly influence implantation rates.
While both day 3 and day 5 embryo transfers have their pros and cons, the decision depends on individual circumstances and goals. Additionally, frozen embryo transfers may offer higher implantation success compared to fresh transfers. Understanding these elements can help maximize the chances of a successful pregnancy through IVF.


