Pregmune

What is Pregmune?
Pregmune is a reproductive immunology assessment report specifically tailored to fertility that can be used to help guide the reproductive immunology treatment managed by your fertility care provider. The Pregmune testing regimen and report were developed by Dr. Andrea Vidali, a Reproductive Immunologist who is highly regarded by the medical team at CNY Fertility.
The Pregmune PGM-1 Reproductive Immunology Assessment Report helps to identify potential factors that may be affecting fertility for both men, women, and couples.
The Pregmune PGM-1 Reproductive Immunology Assessment Report starts with an array of blood tests. The results from the tests are then analyzed using a sophisticated algorithm designed to detect significant immunological deviations and provide tailored treatment recommendations. All of the testing involved in the Pregmune panel leads up to one thing, a reproductive immunology assessment report.
Why Pregmune Testing?
The implantation of an embryo as well as the maintenance of pregnancy are complex immunological processes. In order for a pregnancy to occur normally, the body has to block the natural process of rejecting a foreign body (the fetus).
This sounds strange, but a fetus is indeed a “foreign body” and “should be” perceived as an invader by the mother’s immune system as its genetic makeup is also includes DNA from the father.
By identifying potential and often overlooked immunological causes of reproductive failures, Pregmune testing provides physicians with helpful and otherwise unavailable information that can be used to create individualized treatment protocols designed to increase the chances for a successful full-term delivery.
Pregmune test results can be used to make pharmacologic, fertility treatment, hormonal/metabolic, and even nutritional recommendations which may improve treatment and pregnancy outcomes.
Who is Pregmune Recommended for?
Pregmune is primarily recommended for those with recurrent implantation failure and pregnancy loss, though others may also benefit from testing.
Individuals with the following conditions may also consider Pregmune testing:
- Poor embryo quality
- Recurrent pregnancy loss
- Stillbirth
- Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia or preterm labor
- Autoimmune diseases
- Endometriosis
- PCOS
- Diminished ovarian reserve
What is Included in the Pregmune Immunology Assessment Report?
- The Pregmune immunology assessment report starts off with a brief patient history and demographics section.
- After the demographics section, there is a results summary page which includes a predicted live birth success rate, brief summaries of the Parental Compatability, Female and Male assessments (detailed later in the report), and a recommended actions section.
- After the summary page, the report goes into a detailed breakdown of the three main components, (1) The Parental Compatability Assessment, (2) The Female Assessment, and (3) The Male Assessment. These sections include breakdowns of each test performed with an explanation of the results, how it impacts fertility/health, and recommendations (when applicable).
Pregmune testing looks at and identifies if any of the following may be affecting fertility:
- Parental Compatibility (HLA mismatches)
- Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxic Activity
- Systemic Inflammation
- Thrombophilia
- Regulatory T-cell
- Autoimmunity
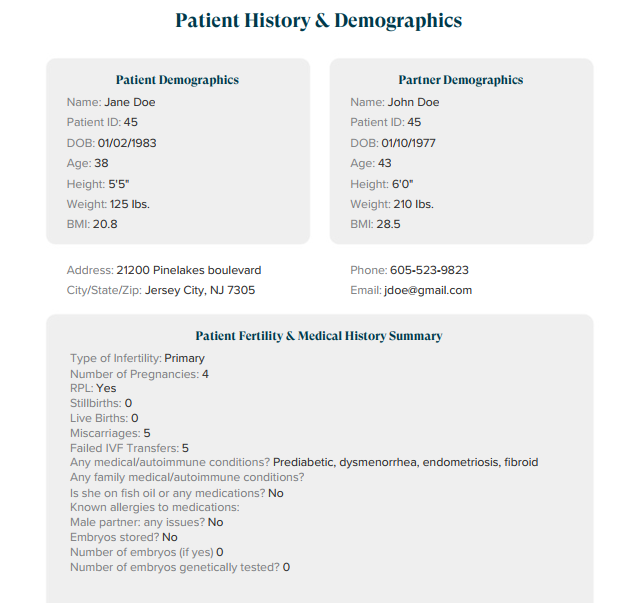
Patient History and Demographics
The patient demographics section includes basic information on both the male and female partners like their ages, height, weight and BMI. It also includes a summary of the patient’s medical and fertility history. Please find a sample demographics and history report below:
Results Summary
As mentioned above, the results summary section of the Pregmune Immunology Assessment Report includes a predicted live birth success rate and summaries of the three main components of the report, the Parental Compatibility, Female and Male assessments. It also includes a recommended actions section which draws information from all of the assessments.
The live birth success rate is based on a customized artificial intelligence algorithm. The predicted Live Birth Success Rate tells you the likelihood of a successful full-term delivery assuming the implementation of all recommended follow-up care included in the assessment portions of the report. The calculation is generated using Pregmune’s customized algorithm based on a source data set of over 1000 patient observations (patients using their own egg and less than 45 years old).
Pregmune testing has three classifications for live birth success rates: (1)Below Average, (2)Average, and (3)Above Average.
Below we will break down the assessment portions of the report.
WARNING: THE REMAINDER OF THIS ARTICLE IS HIGHLY TECHNICAL. PLEASE BE AWARE THAT YOU MAY NOT UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE INFORMATION PROVIDED BELOW, AND THAT YOUR CLINICAL CARE TEAM WILL HELP GUIDE THE TREATMENT APPROPRIATELY.
Parental Compatibility
Pregmune’s parental compatibility assessment determines your risk for defective placentation by assessing the type of protein KIR (expressed on your uterine NK cells) as well as your and your partner’s HLA-C genotype. Further, the level of HLA homozygosity and the degree of HLA allele sharing modulates maternal immune tolerance towards the embryo thus impacting chances for a successful pregnancy.
The Parental Compatability Assessment looks at all of the following:
- Fetal HLA-C and maternal KIR (uterine NK cell) interaction
- HLA Mismatches
- HLA Homozygosity
- Anti-HY Immunity
- Anti-HLA Antibodies
- Embryo MTHFR prediction and Risk for implantation failure
Fetal HLA-C and Maternal KIR (uterine NK cell) Interaction
Research indicates that uterine natural killer (uNK) cells, are involved in the process of normal placental formation and the ability to carry a pregnancy to term.
Uterine natural killer cells (uNK) secrete a unique repertoire of cytokines and growth factors that regulate blood vessel growth and development (also known as spiral artery remodeling) leading to a healthy placentation that supports embryo growth. This secretion is modulated based on the type of interaction (activating or inhibitory) taking place between your KIR receptor (present on the surface of uNK) and the HLA-C of your embryo (inherited from both partners).
This test aims to predict the risk you may have for a placental dysfunction that can lead to miscarriage and pregnancy complications.
HLA Mismatches
Research indicates that matching HLA alleles between male and female partners significantly increases the risk for fetal loss.
A certain level of difference between the mother’s and father’s HLA alleles (inherited by the embryo and defined as a mismatch) is necessary to actively generate immune tolerance of the embryo. Thus, couples with a low number or no mismatched alleles for HLA genes may be more prone to infertility, repeated implantation failure, and recurrent pregnancy loss.
Pregmune testing checks for the lack of HLA class II allele mismatching which could impact the ability of the maternal immune system to generate tolerance for paternal antigens present on the embryo.
HLA Homozygosity
Homozygosity of HLA class II alleles leads to a limitation in the repertoire of paternal class II antigens that can be presented to the maternal immune system. Thus, your immune system does not generate tolerance for paternal antigens found on the embryo, in the most optimum way. The more alleles diversity there is, the better it is.
Pregmune testing checks the female patient’s risk for failure to generate immune tolerance towards paternal antigen found on the embryo by measuring the significant homozygosity of class II alleles.
Anti-HY Immunity
Research indicates that maternal carriage of HY-restricting HLA class II alleles decreases the long-term chance of live birth in women after they have previously delivered a boy.
Healthy women, pregnant with a boy, may generate an immune response against HY antigens (male-specific minor histocompatibility antigen). Women with a firstborn boy and carrying HY restricting HLA allele (HYrHLA alleles) have significantly reduced chances for a subsequent live birth.
Pregmune testing checks the patient’s risk for triggering the development of anti-HY responses
Anti-HLA Antibodies
Your immune system (B cells) can target paternally derived HLA molecules, present on the embryo. HLA antibodies are commonly found in pregnant women and paternal-specific anti-HLA antibodies are considered harmless during most pregnancies. Nevertheless, they have been associated with early miscarriages, obstetrical complications, and secondary infertility. They may denote a particular ability from the maternal immune system to develop an aberrant immune response to paternally derived antigens.
Embryo MTHFR Prediction and Risk for Implantation Failure
Research indicates that homozygote form of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase(MTFHR) mutation is a significant risk factor for recurrent IVF failure.
Your MTHFR genotype (both partners) can help predict your risk of having embryos carrying two copies of the T allele. This genotype has been associated with a failed implantation in patients experiencing recurrent pregnancy losses and/or recurrent implantation failures.
Pregmune testing checks the couple’s probability of having an embryo carrying MTHFR T/T mutation, which helps to determine the risk for failed embryo transfer.
The Female Assessment
Pregmune’s female assessment is an extensive panel of tests that determines if your thyroid function, hormonal and inflammation levels are within the optimal range. It determines your risk for autoimmunity (production of antibodies potentially attacking your own body or your baby), as well as your risk for blood clot formation. The panel also determines whether your diet is balanced or if it may trigger inflammation by looking at your free fatty acid, folic acid, and Vitamin D levels.
In short, the female assessment looks at the following:
- Chromosome Analysis
- Thrombophilia
- Autoimmunity
- Thyroid
- Serological
- Inflammatory
- Metabolic
- Nutritional Analysis
Below we will examine each area of the female assessment in detail.
Chromosome Analysis
Chromosomal abnormalities contribute to approximately 5–10% of reproductive failures. Research indicates that chromosomal analysis can be used as a diagnostic tool to assist in proper reproductive counseling.
A karyotype (or chromosome analysis) is a test that evaluates the number and the structure of your chromosomes (genetic blueprint) to detect any abnormalities.
Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia increases your risk of blood clots and is also linked to several other conditions. Pregmune testing checks for the presence of thrombophilia and these other conditions like Hyperhomocysteinemia (high homocysteine levels).
Pregmune’s thrombophilia testing checks all of the following:
- MTHFR (5, 10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) activity
- Homocysteine level
- PAI-1 4G/5G Polymorphism
- Prothrombin Factor II 20210
- Factor V (Leiden) mutation 1691
- NR, PT and aPTT
Research indicates that there is a significant relationship between inherited thrombophilia, unexplained infertility, and recurrent pregnancy loss.
Autoimmunity
Reproductive autoimmune failure can be associated with overall activation of the immune system or with immune system reactions specifically directed against ovarian antigens.
Pregmune testing measures several factors related to autoimmunity, including:
- HLA Autoimmune Disease Predisposition
- Antiphospholipid Antibodies (APAs)
- Antinuclear Antibodies
- Anti-CCP Antibodies and Rheumatoid Arthritis Factor
Thyroid
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your throat. It is a key regulator of your hormones production and its optimal function is crucial during pregnancy. It also helps to keep your metabolism in check, regulates your heart, body temperature, and digestive system.
Resrach indicates that severe thyroid dysfunction may lead to menstrual disorders and infertility via direct and indirect interaction with the reproductive organs.
Pregmune testing checks that thyroid hormones are all within normal levels and also that no thyroid antibodies are detectable.
Serological
Pregmune testing measures a patient’s white blood cell count and platelet count to ensure they are within the normal range.
Your white blood cell (WBC) are part of your immune system and help fight infections.
Platelets are essential for normal blood clotting. Determining your levels will help detect some health issues.
Inflammation
Inflammation is becoming increasingly linked to reproductive dysfunction and several common infertility-related conditions like Polycystic Ovarian Syndrom (PCOS), Endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and more.
Pregmune’s inflammatory testing measures all of the following:
- Total Immunoglobin levels
- Complement Activity (C3 and C4 levels)
- TH1:TH2 intracellular cytokine ratio
- Natural Killer Cell Activity (NKa) levels
- Regulatory T Cells (Treg cells) levels
All of the above either play a key role in immune system function, autoimmune diseases, or inflammation; all of which likely impact one’s chances of getting pregnant.
Metabolic
Pregmune’s metabolic testing is an Insulin Resistance and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Assessment.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine condition, commonly characterized by high levels of androgens and resistance to insulin.
Women with PCOS experience high levels of infertility and are at increased risk for pregnancy complications such as gestational diabetes and hypertension.
This test screens for many hormones that may help diagnose PCOS.
Nutritional
Pregmune’s nutritional testing checks the following levels which all relate to fertility:
- Vitamin D – this vitamin regulates many factors including the steroid hormones estrogen and progesterone, the immune function and reduces oxidative stress.
- Folic Acid – a compromised folate status in pregnant women is associated with recurrent miscarriages and fetal neural tube defects.
- Fatty Acid – fatty acids can help reduce maternal inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Leptin – Leptin is produced by adipocytes (fat cells) and may play an important role in reproduction.
The Male Assessment
Pregmune’s male assessment draws information from an extensive panel of tests that looks at factors that may be affecting the male partner’s semen quality. It also looks at factors which impact his risk for blood clot formation, which could be passed on to the embryo and resulting fetus. By looking at his free fatty acid levels as well as his MTHFR genotype, the panel determines whether his diet is balanced or if it may trigger inflammation which may be impacting his semen quality and fertility.
Inflammation may affect male fertility in several ways. Research indicates that inflammation within the male genital tract can have a negative impact on sperm quality.
The Male Assessment looks at all of the following:
- Chromosome Analysis – Similar to the Female Assessment. Looking at the risk of chromosomal rearrangements and congenital anomalies.
- Thrombophilia – Similar to the Female Assessment. Looking at the risk of blood clots.
- MTHFR Analysis – Similar to the Female Assessment. Looking at the risk of homocysteine accumulation and inflammation.
- Nutritional Analysis – Deep dive below.
Nutritional Analysis
- Fatty Acid – Research indicates fatty acids can help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress which may help to prevent sperm DNA damage and have a positive effect on overall sperm quality.
- DHA and EPA levels – Research indicates that increased DHA and EPA levels may positively impact sperm motility and concentration.
- Leptin levels – Research indicates that high leptin levels may contribute to reduced reproductive function, especially in obese men.
Pregmune Cost
The cost of Pregmune is highly variable and not billed by CNY Fertility; nor does CNY Fertility have any financial stake in recommending Pregmune.
As such, we highly recommend you obtain written estimates from any entity involved in the Pregmune testing prior to beginning and similarly obtain verification of coverage from your insurance company to see if any of it can be covered by insurance.
Accessing Pregmune
If you are interested in discussing Pregmune with one of our providers and are not yet a patient, you will need to schedule a consultation. If you are already a patient, please contact our clinical team through your patient portal and also click here to schedule a free consultation with Pregmune to learn more.


